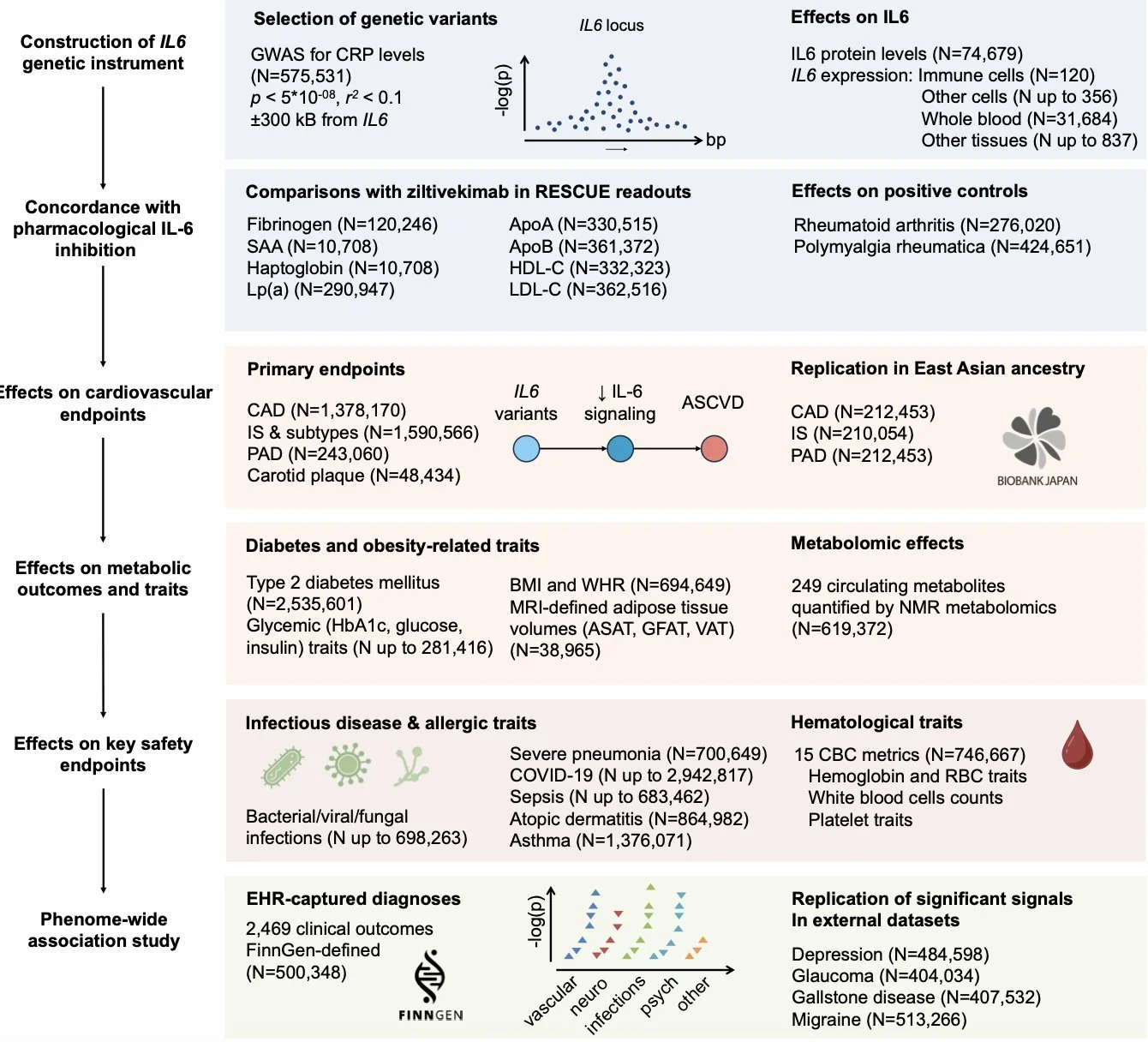
Our work at Nature Cardiovascular Research: genetically proxying IL-6 inhibition
How can human genetic data be leveraged to validate drug targets?🧬 ➡️ 💊
In our latest work in 𝐍𝐚𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐂𝐚𝐫𝐝𝐢𝐨𝐯𝐚𝐬𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐚𝐫 𝐑𝐞𝐬𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐡, we provide an end-to-end framework for genetically validating IL-6 inhibition for cardiovascular outcomes.
𝐁𝐚𝐜𝐤𝐠𝐫𝐨𝐮𝐧𝐝:
Genetic variation in IL6R, the receptor for IL-6, has long been linked to risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), motivating the development of anti-inflammatory therapies targeting IL6 signaling.
However, drugs in development target IL-6, not its receptor raising the question if genetic evidence for IL6R perturbation can be applied to IL-6 inhibition?
𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐰𝐞 𝐝𝐢𝐝:
1️⃣ Using available GWAS data, we developed a genetic proxy (instrument) of IL-6 inhibition based on 12 variants in the IL6 locus associated with CRP
2️⃣ We benchmarked the proxy against clinical trial data (anti-IL6 antibody ziltivekimab) across 8 biomarkers and autoimmune disease endpoints (rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica)
3️⃣ We tested associations with cardiovascular endpoints, showing protective effects for coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, carotid atherosclerosis, and atherosclerotic ischemic stroke
4️⃣ We observed favorable metabolic effects, including an association with lower risk of type 2 diabetes and changes in lipid profile, mainly increases in HDL particle metrics
5️⃣ Given the known immunosuppressive effects of IL6R inhibition, we examined associations with infectious diseases. Unlike the IL6R proxy, our IL-6 inhibition proxy showed no strong signal for increased infection risk. In fact, it was associated with a lower risk of pneumonia hospitalization.
6️⃣ In a phenome-wide analysis (PheWAS) in FinnGen, we replicated the protective effects of the IL-6 proxy across major cardiovascular, metabolic, autoimmune, and respiratory endpoints and also revealed risk-lowering associations with depression and gallstone disease
7️⃣ We identified safety signals of potential relevance for specific populations, including glaucoma, migraine, and maternal perinatal/postpartum hemorrhage, warranting further investigation.
Great work by Lanyue Zhang, Murad Omarov and Lingling Xu. Grateful for the collaboration with Emil deGoma from Tourmaline Bio (developing an anti-IL6 antibody) and Pradeep Natarajan!
🔗 link to the paper (open-access🔓): https://www.nature.com/articles/s44161-025-00700-7
Also, an excellent summary of the nuances and implications of our work in an accompanying editorial by Michael Shapiro
https://www.nature.com/articles/s44161-025-00702-5